Last Updated on August 13, 2020 by Allison Price
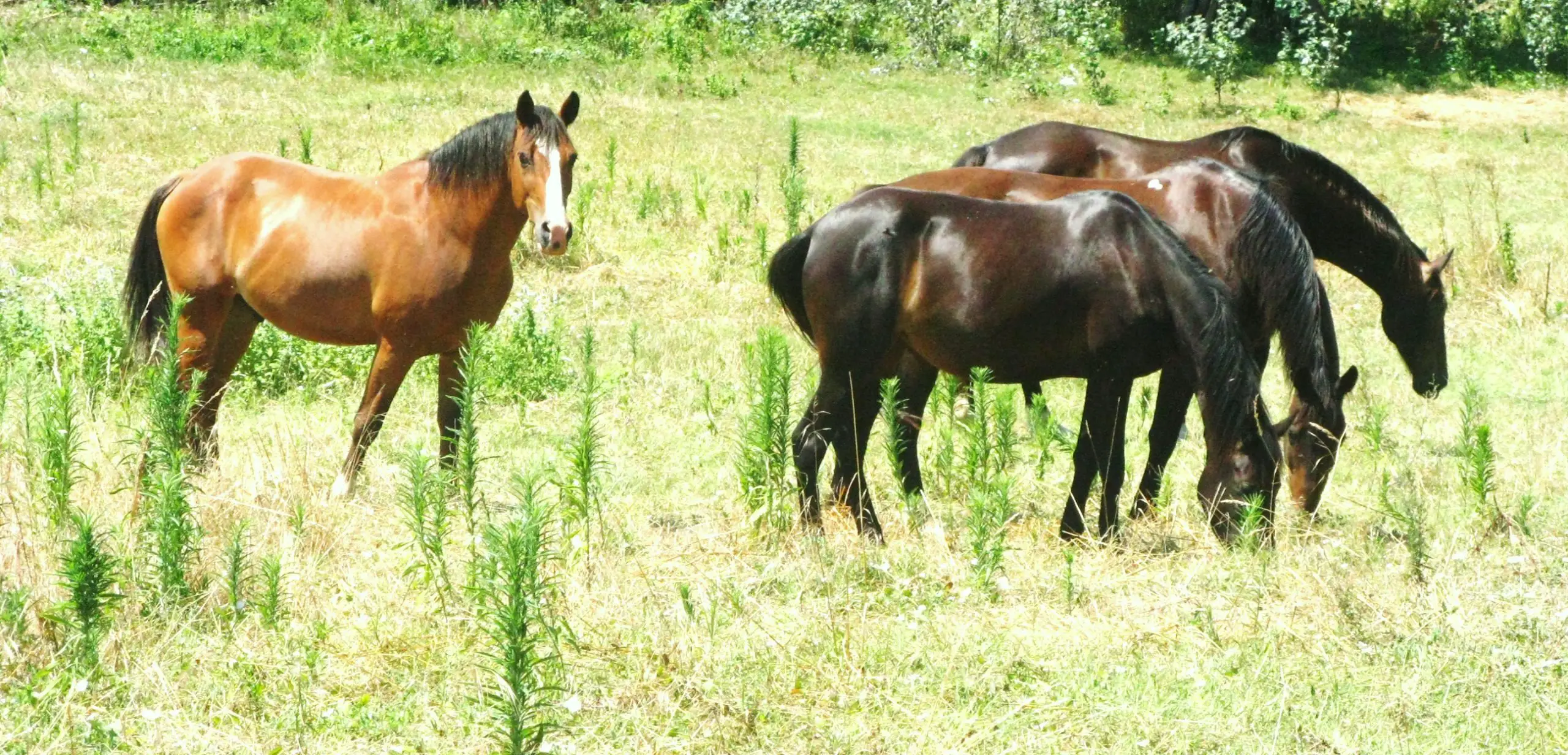
It is not uncommon for horses to get infected by pest and parasites on a normal basis, but how should you deal with it? Parasites can cause acute medical problems as well as chronic debilitation. They may be responsible for diarrhea, intestinal impact (colic), and poor performance. One type of parasite that infects most horses is then called pinworms.
What Are Pinworms?
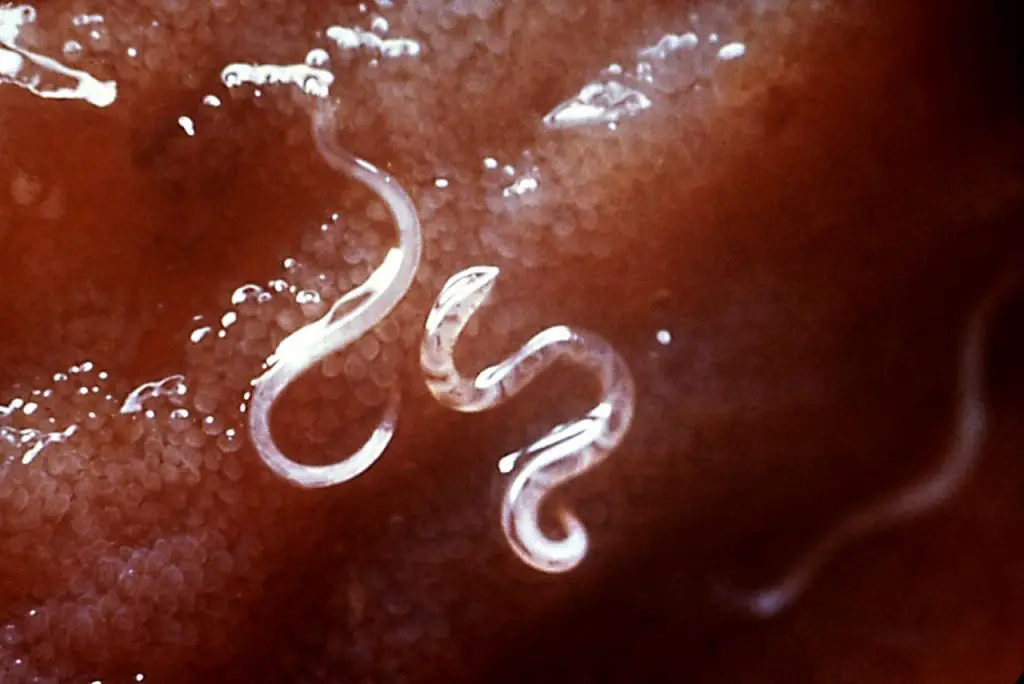
Adult pinworms are white worms and can grow as long as 15cm. They usually live in a horse’s right dorsal colon. Female pinworms lay yellow eggs around the horse’s anus to perianal pruritus (itching of the tail). Afterwards, they die. A sticky substance with the eggs is usually found around the infected horse’s anus. This leads to the worm being then passed in droppings. In three to five days, dislodged pinworm eggs will become infectious.
How do Horses Get Infected by Pinworms?
Pinworms’ life cycle is different from other parasites in the gastrointestinal system. The one that causes infection is its eggs. Horses get infected when they swallow pinworm eggs. It happens if they come in direct contact with the eggs from an infected horse. It can also happen if they happen to swallow the eggs on pasture or hay that have fallen off from an infected horse. There is no intermediate host in the body, and no migration by any other organ.
Signs and Effect of Pinworms
A horse that always rubs its butt is the most common clinical symptom of pinworms. Pinworm is then found with colic. Also, it is visible with horses suffering from appetite loss and severe depression.
Can you see worms in horse poop? There are instances that you will. You might see the parasites themselves in the droppings. It is unusual the horses have worms. Usually, pinworms metabolized in the gut. If you see the worms, you need to identify and treat them with the appropriate wormer.
Where does the itch come from? Pinworm uterine fluid in their eggs can cause skin irritation. Either by direct contact, or through immunological reaction, all these can cause itch. This may explain why some horses itch severely while others show no reaction.
How to Treat Pinworms
Natural Treatment
Any toxic load on animal system will compromise the liver and kidney. These chemicals are then cleaned out of the system via the normal metabolic process. Any toxic that is not removed is usually stored in fat. It will be then released out from the system through poop. Herbs is usually used to help detox from the negative effects of chemical drenching. Helping your animal manage worm loads is a realistic goal and is then done using a variety of approaches.
We have listed, few common alternative aids. These have anti parasitic and vermicide effects.
- Wormwood
- Chinese Rhubarb
- Tansy, Burdock
- Flax Seed
- Cloves and Garlic
Create a mixture of traditional anti-parasitic herbs. It is best to choose the one that works by toning up the gut wall while helping remove worms at the same time. Daily use makes the gut safer than ever and horses are more capable of handling normal worm load. These herbs are usually mixed with raw apple cider vinegar. Specific dosages are then given in a set program over weeks.
Tip:
Aloes, Elecampane and slippery elm powder is usually used to heal damage to the lining of the gut. This makes the environment and GIT ecology much healthier.
Note:
These Natural Treatment is an alternative aid for horses that are very sensitive. There is no herbal remedy that can kill all worms and record a blood test with a zero count. Worms developed along with the digestive ecology of all animals. Any infestation can be regulated with cleanliness and proper care so that it does no harm to the animals.
Managing the Environment
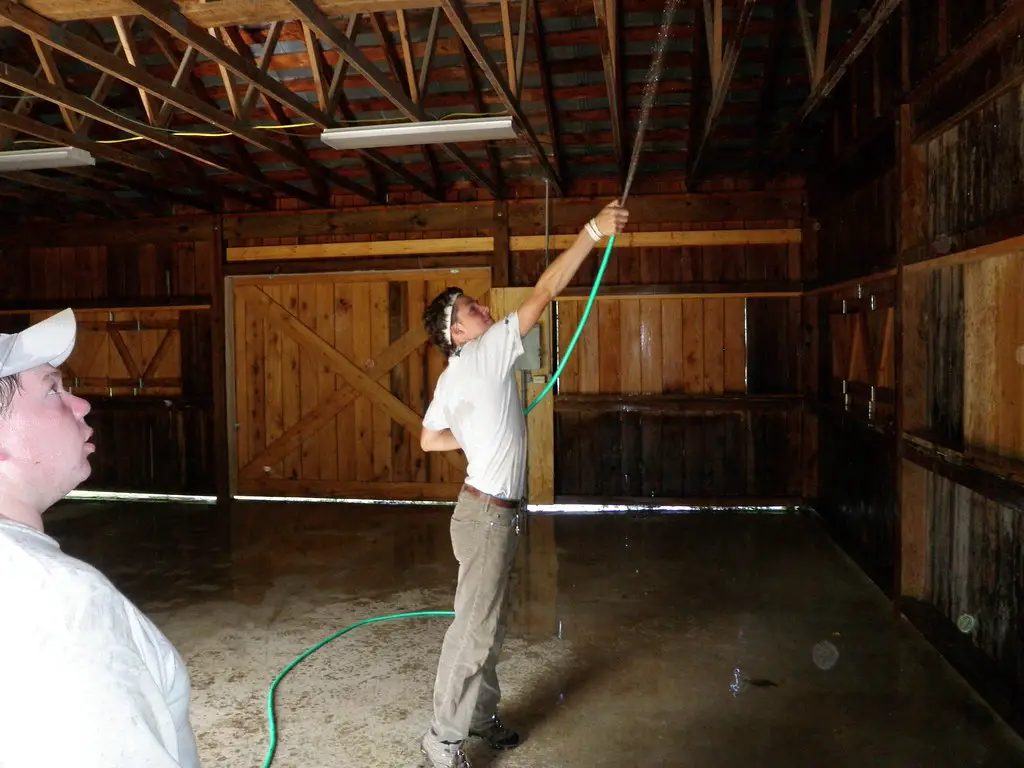

Managing the environment is still considered as a natural remedy. Worm cycles are usually interrupted by dry periods and frost. Thus, the likelihood of herd infestation is then lowered. Always, keep the manure under control. This is especially if you have a high animal population on small acreage. Make sure you allow good rest periods in paddock. Follow proper methods of grazing (with sheep or cattle) is always recommended. You can use bio dynamic soil sprays, basalt, and dolomite. This is to condition the soil is also part of managing the whole system in balance.
Clinical Treatment
Chemical wormers are very strong as they kill worms quicker than killing the host. If pinworm is then confirmed, treat your horse with an oral wormer that pinworms are sensitive to. Pyrantel based wormers like Strongid-P used by a double dose. This should be then repeated every six to eight weeks. After cleaning, you can apply Vaseline on the skin surrounding your horse’s bottom after cleaning. This will help reduce the number of eggs that stick to the skin. In US and New Zealand, pyrantel or oxfendazole only killed adult pinworms. These are pinworms who had survived treatment with ivermectin or abamectin.
However, IF SYMPTOMS PERSIST, CONSULT VETERINARIAN FOR BETTER DIAGNOSIS & PROPER TREATMENT.
Sellotape Test Procedure
Another way to test for pinworm is to take a sellotape impression from under the horse’s tail. Sellotape is a sticky tape test for worms.
To do this, take a 4 “long, clear sticky tape and firmly press it onto the skin around the anus (not the hair). Collect the sample in the morning, ideally before 9 am. Pinworms are most active at night. Thus, this will give the best chance of detecting any activity that is present. Fold the tape in half and on the sticky side. For best results, perform the tape test three days in a row, and then take the pieces of tape to your veterinarian. Your vet can look at the tape under a microscope to see if there are any pinworm eggs.



